
October 25, 2022
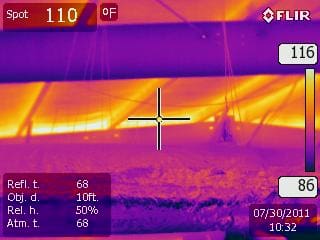
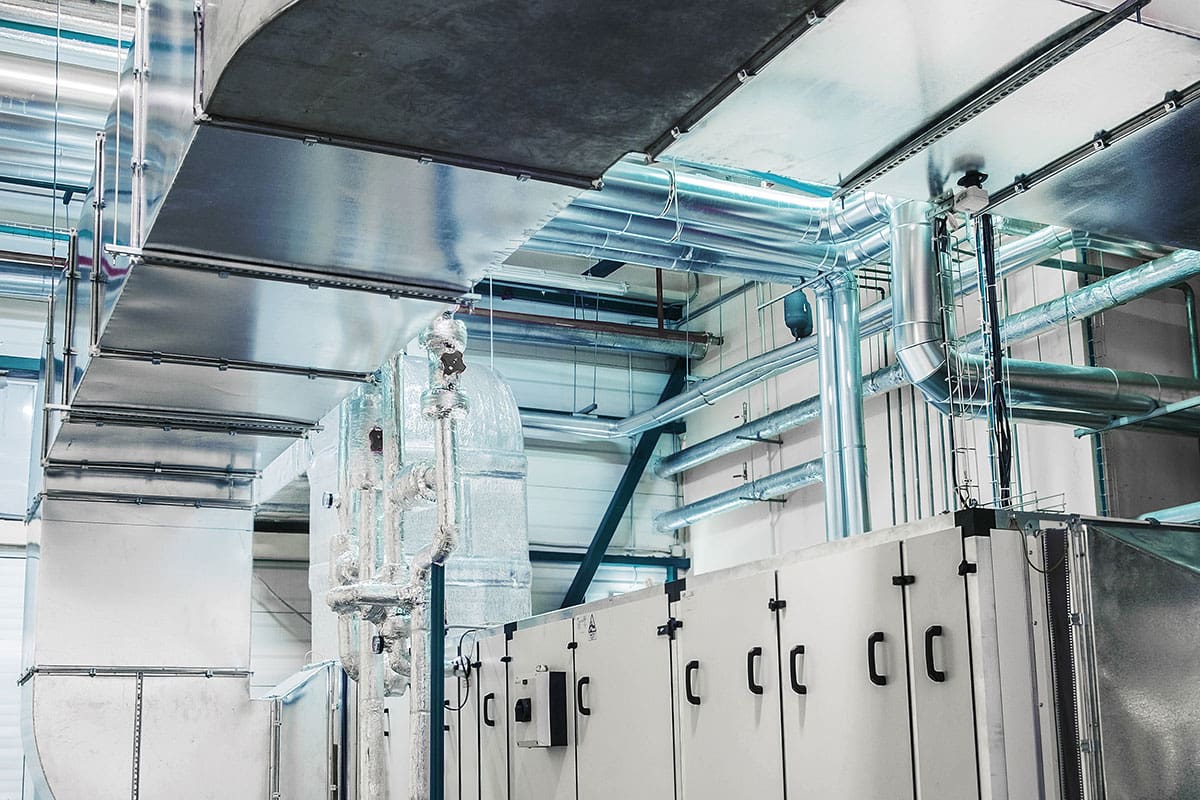
What’s involved in a good thermally tuned image. Let’s talk about FORD. In thermal imaging, FORD is not a car or a truck – it stands for Focus, Range, and Distance. Let’s review some parameters, we need to be concerned with when taking or analyzing a piece of equipment or building. The first step to performing a good analysis of a thermogram is to make sure that you have a good thermogram to analyze. So now we need to talk about FORD, remember FOcus, Range and Distance. The thermogram must be in focus, be taken with the correct temperature range and with an appropriate working distance to the target for the lens and infrared camera being used to capture the image. These factors are required, along with having the correct emissivity – which is the single-most important attribute necessary to obtain an accurate thermal measurement. All the above listed parameters are critical to achieving a thermally tuned image.
So what is “Thermal tuning”? The method of manually adjusting specific parameters to produce a thermogram where the colors within the image are spread over the object of interest with the intent of locating fine thermal detail and identifying thermal gradients.
Critical parameters for a thermally tuned image include:
- Focus – the clarity or distinctness of an image rendered by an optical system “in focus”, “out of focus”.
- Range – the lowest and highest temperatures that can be imaged and / or measured with an IR camera’s setting.
- Distance – the appropriate working distance to the target or object.
- Emissivity – the ratio of energy emitted by an object to the energy emitted by a black body at the same temperature.
The benefits of a thermally tuned image could include:
- Reduction of unscheduled power outages.
- Detection of problems quickly, without interrupting service.
- Assessing priorities for corrective action.
- Minimizing preventive maintenance and troubleshooting time.
- Checking for defective equipment while still under manufacturer’s warranty.
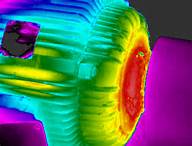
When obtaining images of mechanical systems, a thermally tuned image can:
- Inspect burners and boilers for flame impingement and burner management.
- Scan and record temperatures in areas of boiler not monitored.
- Assist with mechanical bearing inspections.
- Monitor belts and sheave wear.
- Assist with HVAC equipment evaluation.
- Detect insulation leaks in refrigeration equipment.
- Detect uniform cooling of Dx and chilled water coils.
- Detect potential leaks in ductwork.

